29 April 2019 by Remco Bouckaert
There are a number of handy utilities in the Babel package, which can be launchers with the AppLauncher that comes with BEAST. After you installed the Babel package, you can start them by selecting File >> Launch Apps menu in BEAUti, or you can start them from a terminal, by passing the App name to the applauncher program that comes with BEAST. For instance, if you want to convert a NEXUS tree file to Newick tree file, you do so using
Windows:
\path\to\BEAST\applauncher Nexus2Newick -trees nexus.trees -out newick.trees
OS X:
/Applications/BEAST\ 2.5.2/bin/applauncher Nexus2Newick -trees nexus.trees -out newick.trees
Linux:
/path/to/beast/bin/applauncher Nexus2Newick -trees nexus.trees -out newick.trees
where \path\to\ and /path/to/ is the directory where BEAST is uncompressed on Windows and Linux respectively.
Babel has the following Apps:
- CladeSetComparator to validate tree sets converged to the same distribution
- LineagesThroughTimeCounter for creating LTT plots
- SpanningTree for sanity checking cognate sets
To manipulate trees
- AdjustTipHeight
- LeafSplitter
- TreeGrafter
- TreeRelabeller
- TreeTransitionMarker
- MakeUltraMetric
- TreeEpochScaler handy when you have deep branches, but most of the detail is from recent splits.
- FamilyFilter
Converting file formats
- Nexus2Newick
- Newick2Nexus
- Phy2Nexus
More details below.
CladeSetComparator
Match clades from two tree sets and print support for both sets so they can be plotted in an X-Y plot
tree1source tree (set) filetree2source tree (set) fileoutoutput file, or stdout if not specifiedsvgsvg output file. if not specified, no SVG output is produced.burninpercentage of trees to used as burn-in (and will be ignored)
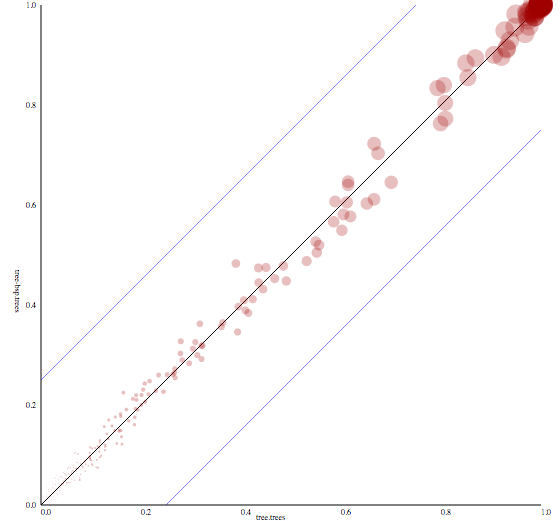
Output produced by CladeSetComparator plotting the clade support of one tree set against another. The blue lines indicate a 25% offset from the x-equals-y line. Trees from the time stamped data tutorial.
LineagesThroughTimeCounter
Produce table for lineages through time plot with 95%HPD bounds
treesNEXUS file containing a tree setoutoutput file. Print to stdout if not specifiedsvgoutif specified, produce SVG file with graphburninpercentage of trees to used as burn-in (and will be ignored) resolutionnumber of steps in table reverseSVGAxisreverse x-axis, that is go forward in time instead of backwardmaxXmaximum value for x-axis. Automaticlly deduced if < 0 maxYmaximum value for y-axis. Automaticlly deduced if < 0
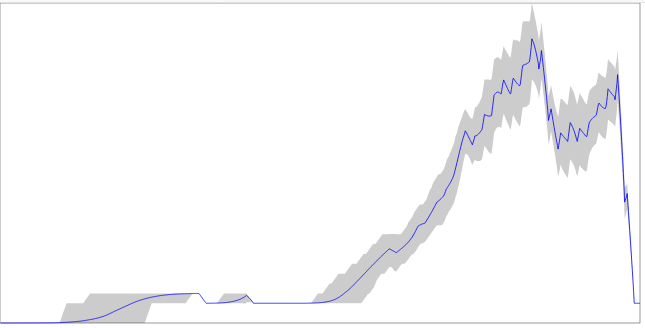
Lineage through time plot for human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup A (using trees from time stamped data tutorial).
SpanningTree
Creates spanning trees of cognate sets.
nexusnexus file containing cognate data in binary format kmlkml file containing point locations of languages cognatecognate file listing labels for each column backgroundimage map in mercator projection used for background maximumDistancemaximum distance to split on
Converting file formats
Nexus2Newick
Convert nexus tree file to Newick format
treesNEXUS file containing a tree setoutoutput file, or stdout if not specified
Newick2Nexus
Convert Newick tree file to NEXUS format
treesNewick file containing a tree setoutoutput file, or stdout if not specified
Phy2Nexus
Convert phyml phy format to nexus alignment file
phyPhyml phy file containing a sequence set outoutput file, or stdout if not specifieddatatype
Manipulating sets of trees
AdjustTipHeight
Set tip heights of existing tree to match the heights from a list
treesNewick file containing a tree setcfgtab separated configuration file containing two columns: column 1: name of taxon, column 2: height (age) of taxon outoutput file, or stdout if not specifiedyear2millenium
LeafSplitter
Relabels leafs of tree set, and splits leafs into random binary sub-tree with branch lengths exponentially distributed.Output as newick trees (not nexus). Metadata is not preserved.
labelMapspace delimited text file with list of source and target labels. For taxa that need splitting, specify a comma separated list of new taxon labels. meanLengthbranch lengths are drawn from an exponential with average meanLength treesNEXUS file containing a tree setoutoutput file, or stdout if not specified
TreeGrafter
Grafts nodes into a tree above the MRCA of a set of nodes. This can be useful in case there are taxa that are not part of the analysis, but for which we know from prior information where a taxon should be placed (e.g., South African language in an Indo-European langagae analysis).
cfgtab separated configuration file containing three columns: column 1: name of taxon column 2: height (age) of taxon column 3: a comma separated list of taxa determining MRCA to graft above in source tree (if no constraints have been specified). constraintsnewick tree file with constraints on where to insert leaf nodessrcsource tree (set) file used as skeletonoutoutput file, or stdout if not specified
TreeRelabeller
Relabels taxa in a tree file. Usfeful for instance when labels are iso codes and language names are required for visualisation
treesNEXUS file containing a tree setoutoutput file. Print to stdout if not specifiedlabelMaptab delimited text file with list of source and target labels
TreeTransitionMarker
Mark specific transitions of a meta-data attribute on a tree to make it easy to visualise these transitions, e.g. for an ancestral reconstruction analysis
treesNEXUS file containing a tree (set)outoutput file. Print to stdout if not specifiedtagmetadata tag to be marked frommetadata tag value at top of branch to be marked tometadata tag value at bottom of branch to be marked markAll
MakeUltraMetric
Converts a rooted tree (set) to an ultrametric tree (set), i.e., make all leafs have same distance to root by extending leaf branches so the height of all leaf nodes is zero.
treesNEXUS file containing a tree setoutoutput file. Print to stdout if not specified
TreeEpochScaler
Scales trees so epochs have the same length. This is handy when you have deep branches, but most of the detail is from recent splits: say your tree has a very long branches to the root, and you want to display it well in FigTree then you can define two epochs: one from the root to the oldest child, and one from that child time till present.
treesNEXUS file containing a tree setoutoutput file. Print to stdout if not specifiedepochsspace delimited list of epoch boundaries: each epoch will be scaled to the same height as the first epoch
FamilyFilter
Filters all leafs from specified taxon sets out of a tree file based on clade membership
familiesNEXUS file containing taxon sets treesNEXUS file containing a tree setsubsettext file with list of taxa to include outoutput file. Print to stdout if not specifiedverbose
